Exchange Consolidated Clinical Document Architecture
(C-CDA)
About this Use Case
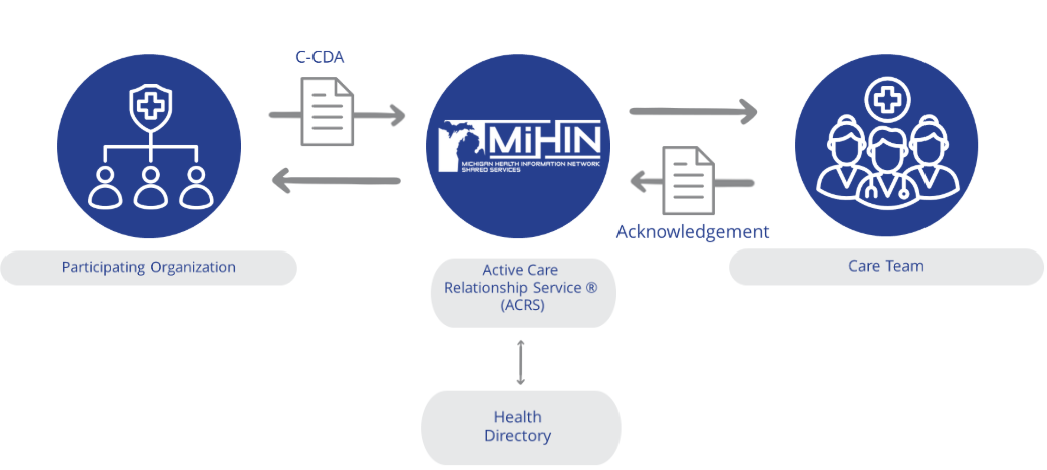
The Exchange C-CDA Use Case supports the exchange of Continuity of Care Documents (CCDs), which summarize a patient’s treatment information following an encounter with a healthcare provider. The data within a CCD is exchanged via a Consolidated Clinical Document Architecture (C-CDA), a standardized, machine-readable HL7 format.
CCDs contain valuable information about the patient, including a comprehensive electronic representation of a patient’s medical history and current conditions. Additionally, a CCD may contain other data elements such as alerts, insurance information, medications, plan of care, vital signs, and much more. This use case ensures that details from a medical encounter at any facility are standardized and accessible to the patient’s care team.
Audience: All healthcare and behavioral health providers, payers, hospitals, and local/state public health agencies